Kotler’s Five Product Level Model and Best PowerPoint Templates
Last updated on September 24th, 2024
When customers buy a product, they are looking to satisfy a need, cater for a want, expect the product to function in a certain way and provide features to work as expected. Businesses that fail to cater to customer needs are unable to attain customer satisfaction. This can only spell ruin for the business. Kotler’s Five Product Level Model sheds light on these aspects and is among the most widely studied models for marketing management. In what is to follow, we will provide you with an overview of Kotler’s model and related PowerPoint templates.

History of Kotler’s Five Product Level Model
Kotler’s Five Product Level model was developed by American economist and marketing guru Philip Kotler. The model was developed by Kotler during the 1960s. Kotler’s model enabled marketing to become an organization-wide operation, instead of being limited to a narrow base of operations. He believed that a product is anything that satisfied a customer need or want. This can even include a retail store or a customer services representative. Kotler’s five product levels aim to satisfy customer needs in light of the five levels described for a product. Understanding these five levels can help businesses satisfy customers and appropriately cater to their needs or wants.
What is a Product?
Before we discuss Kotler’s Five Product Level model, let’s first try to understand what is a product? A product can be defined in different ways. A product can be tangible (e.g. a Soccer ball) or intangible (e.g. insurance policy). A product can be deemed as a commodity which is sold, under set conditions, for a price. A product is sold to cater for customer demand, as well as to satisfy his need(s) or want(s).
What is Kotler’s Five Product Level Model?
The five levels in Kotler’s model include core benefit, generic product, expected product, augmented product and potential product. The core benefit refers to the basic needs or wants of the customer, whereas the generic product are the basic features of a product. Similarly, the expected product is about customer expectations of the product. Augmented product implies the features to differentiate it. The potential product includes the changes to and additions to the product, which might reshape it to make in the future to delight customers.
The Key Components of Kotler’s Five Product Level Model and How to Use Them?
Now that we have a basic understanding of Kotler’s Five Product Level Model, let’s take a look at its key components in detail and how to use them for marketing management.
1. Core Benefits
When you plan to buy a product, you have some core benefits in mind. Be it buying a house, enrolling for a University degree or something you pick at a retail store, you are looking to satisfy a need or a want.
Example: When you buy a smartphone, you expect it to allow you to receive and make calls, take pictures, access the Internet and use various useful apps. These are the core features of the product that are expected by the customer. We can argue that Nokia’s decline was attributed to the fact that while its phones catered for basic customer needs of making and receiving calls, it’s Symbian and Windows Phone-powered phones did not have a variety of apps and features which had become common in other phones. In the end, it failed to give customers value for money and even the core benefits they desired.
2. Generic Product
This is what makes a basic product made up of only important features. Generic product implies a product with its core features only. This includes something common for such a product, with perhaps a few extra features.
Example: When people buy low-end Android smartphones, many of them provide a generic product with an Android operating system and all its basic features. Some might have a few extra features such as a screen that is above average in size or a battery that lasts exceptionally longer. A generic product is barely enough to make it useful for the customer. Many low-end smartphone manufacturers have either gone out of business or operate with little revenue because they have been unable to go beyond a generic product.
3. Expected Product
This is the customer’s expectations of the product. A customer from a developed country might have very different expectations than someone living in a low- or middle-income country.
Example: A customer from an affluent background might expect a high-end smartphone with a fast processor, extended battery time, large screen, good camera and accessories which are high in quality. A customer who cannot afford an expensive smartphone might be looking for a phone that is cheap with a few basic features. Depending upon the income level and preference of the customer, he might even opt for a phone with a small screen or poor camera, with accessing the Internet and making calls as his main motivation for buying a smartphone.
Companies like OPPO have been successful in capturing the marketing for cheaper smartphones by offering reasonable smartphone features and making up for their low-end cameras with interesting effects that make photos look good. This has made OPPO the fifth largest smartphone producer globally. Many local brands in developing countries are now facing tough competition because of it, whereas Apple continues to remain a product for aspirational consumers and affluent customers globally among the top three largest smartphone makers in the world.
4. Augmented Product
These are the features that make the product different from the competition and give it a distinct identity or value. Augmented product refers to how businesses differentiate their product based on its features.
Example: Apple’s smartphones are distinct with Apple’s proprietary software and accessories. Apple’s iPhones are expected to be of high quality, both in terms of software and hardware, as well as the accessories offered with Apple’s branding. On the contrary, Samsung differentiates its product by using a fork of the Android operating system, with some additional proprietary Samsung apps and hardware, which distinguish it from generic, low-end Android phones.
5. Potential Product
These are the augmentations or added transformations for a product that can make it what it can be in the future.
Example: Many products today appear very different from their humble beginnings a few years back, be it Apple’s iPhones or Samsung’s smartphones. The modern iPhone has a faster processor, better battery, camera and accessories. Furthermore, its app store has expanded beyond anything it was when the first iPhone was released back in 2007. Similarly, Samsung’s smartphones no longer use the Symbian operating system and are much better in terms of software and hardware than what they used to be when Nokia led the global market. The potential of the product, with the right augmentations and transformations, can make or break it.
Kotler’s Five Product Level Model PowerPoint Templates
1. Philip Kotler Marketing New Values PowerPoint Template
This template not only provides slides for making Kotler’s model in the form of PowerPoint slides but also to discuss the needs of new customers to explore the possibility of making a new product or augmenting existing products to transform them into something even better.
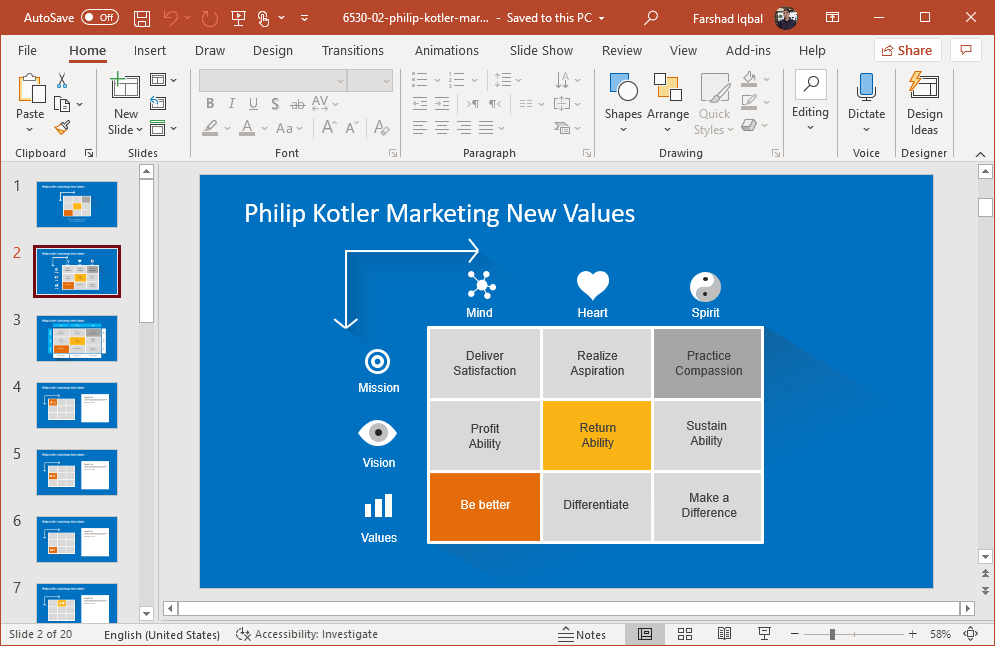
Go to Download Philip Kotler Marketing New Values PowerPoint Template
2. Persona Analysis PowerPoint Template
To make use of Kotler’s model, it is important to understand customer needs and wants. This can be done using buyer personas. You can use a template to create buyer personas, as well as to explain Kotler’s Five Level Product model with the help of customizable slides that are easy to customize according to your topic. Alternatively, this other template can help to easily conduct a buyer persona analysis and present it to an audience or stakeholders.
Go to Download Persona Analysis PowerPoint Template
Final Words
The job of the marketer is not just selling the product but to understand and cater to the actual need or want the product aims to satisfy. A marketer is not selling a smartphone or an air conditioner but rather what needs or wants are satisfied with it. Be it connectivity and fun that a customer might have using a smartphone or the cooling an air conditioner might give amidst scorching heat.
The customer’s minimum and expected utility from the product needs to be met, as well as something extra in the form of augmentations is necessary to lure the customer. Eventually, the product needs to evolve with customer needs with the right transformations over time. This is where Kotler’s Five Product Level model can help businesses understand and satisfy customer needs.
