Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstaller in Windows
Last updated on April 27th, 2024
There are a lot of files in Windows based operating systems which come with restrictions. The TrustedInstaller.exe is a Windows Module Installer service in Windows OS which performs the function of installing, modifying and removing system components and Windows updates. Sometimes, you might require deleting a file or folder managed by TrustedInstaller. In such a case you might not have access to the file or folder. In this tutorial we will show you how to delete files protected by TrustedInstaller in Windows.
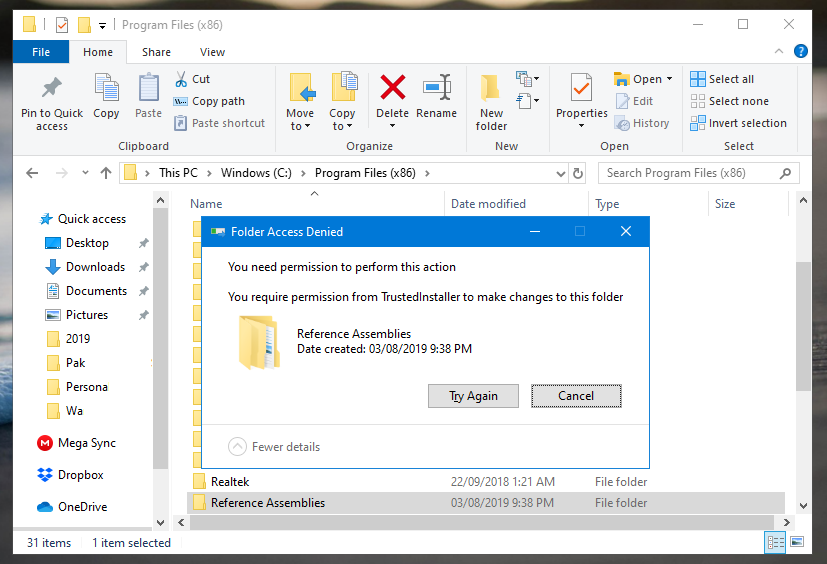
To delete a file or folder protected by TrustedInstaller in Windows, right-click and go to Properties.
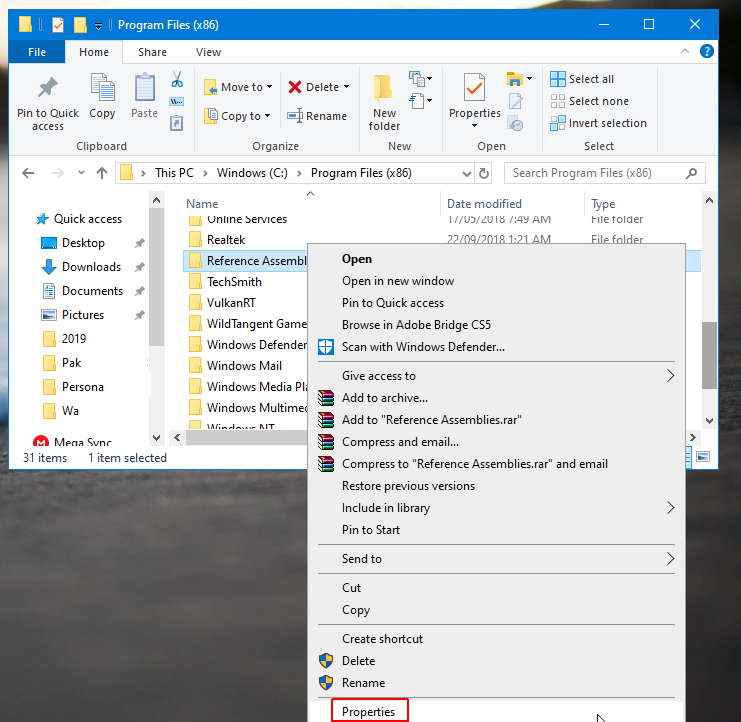
Now, click on the Security tab and head over to Advanced.
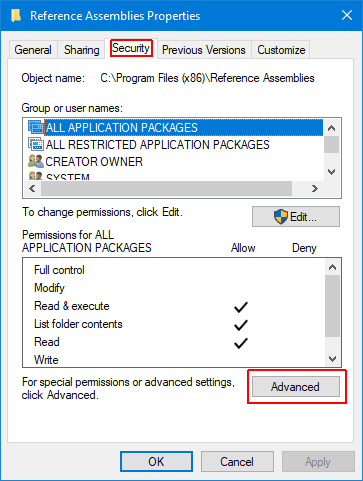
Click Change to proceed further.
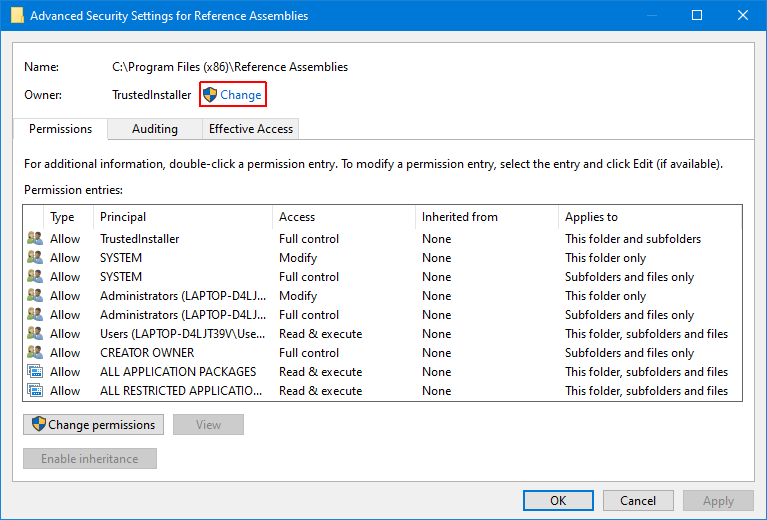
Enter the name of the username you wish to grant Trustedinstaller permissions to and click Check Names. Once the username is shown, click Ok.
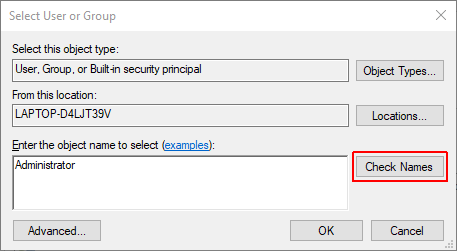
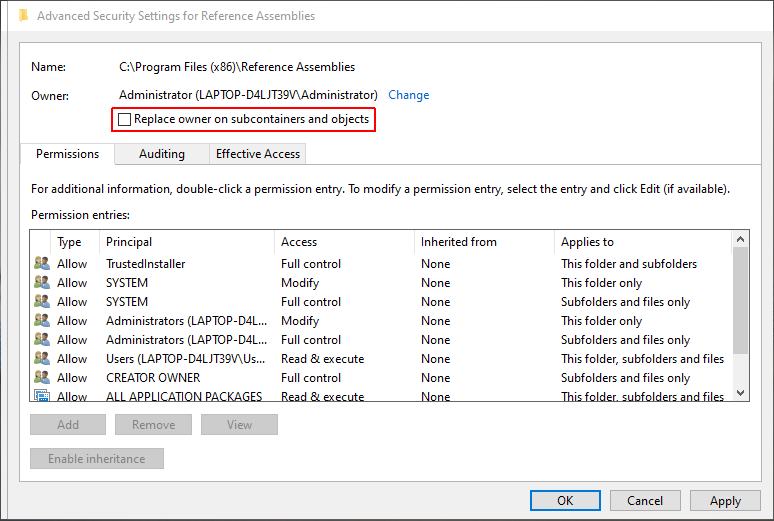
Check Replace owner on subcontainers or objects and click Apply, followed by Ok.
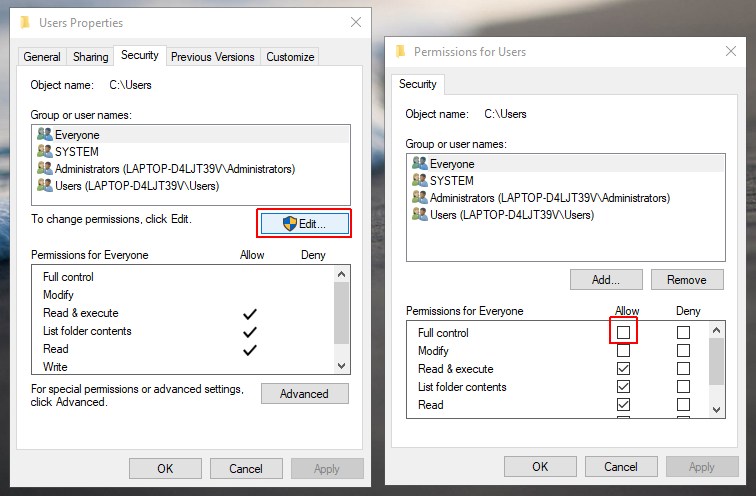
In the next step, select the account from Group or user names that you wish to grant access to and click Edit, followed by Full Control (as shown below). This will grant complete access to your selected username. Click Ok to close the dialogue boxes (as needed).
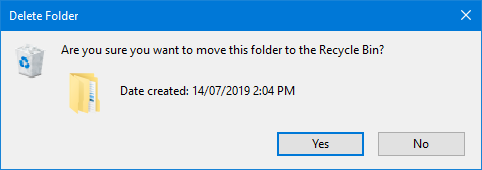
Now that you have ownership of the file or folder, you can delete it like any other document.
Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstaller – Video Tutorial
In some situations you require permission from TrustedInstaller to perform some actions. The above mentioned process is also explained in the video given below. The video gives you a step-by-step walkthrough of the process for taking ownership from TrustedInstaller so that you have the necessary control to delete files using a standard user account.
It is worth mentioning here that deleting protected files and folders can have undesired effects, so make sure you don’t delete anything that can cause system instability. Always backup your data before deleting files and folders which you might suspect can cause operating system issues.
